SLAX is a lightweight version of Slackware Linux. It is fast, customizable, and quite functional when installed on a bootable USB flash drive. This section covers steps for preparing the flash memory device and copying system files to the device. Though illustrating a SLAX install, the procedure works with any live Linux distro.
Here are step-by-step instructions for manually installing Linux on a USB drive and booting with GRUB.
Supplies needed are:
- A suitable Linux distribution, such as SLAX, BackTrack, Ubuntu, or Darn Small Linux.
- A USB flash memory stick, at least 1GB in size (must hold OS plus your data files)
- Disc image editing software for your PC (i.e. MagicISO for Windows; ISOmaster for linux.
Important: Make sure your computer\'s boot sequence (in BIOS Settings) lists CD/DVD devices prior to USB devices, and then your hard drive.
- Download the live Linux ISO file onto your hard drive.
- Download
grubfolder.zip, unzip it, and open "menu.lst"
in a text editor. Scroll to the bottom of the file
and remove (or comment out) the title, kernel, and
boot lines for systems you don\'t have. For example,
if you are going to use only SLAX, delete the
Knoppix, Backtrack, and Bluewhite64 entries. Save and close the edited
file. The "grub" folder will be used in step 5.
title SLAX 6.0.8
root (hd0,0)
kernel /boot/slaxboot/vmlinuz vga=791 ramdisk_size=6666 root=/dev/ram0 rw copy2ram autoexec=xconf;telinit~4
initrd /boot/slaxboot/initrd.gz
boot
- For SLAX installations, obtain also the "GRUB" and either the "GParted" or "QTParted" modules. Knoppix and Ubuntu come with GRUB and QTParted pre-installed :-)
- For SLAX installations, use your ISO editor to place the modules into the /slax/modules folder.
- Using your ISO editor, place the "grub" folder (unziped) from your hard drive into the flashdrive\'s "boot" folder.
- Save the edited ISO with a unique name (don\'t alter the original).
- Burn the ISO onto a blank CD or DVD.
- Reboot into the newly burned live Linux disc.
- When the system is up, insert the flashdrive.
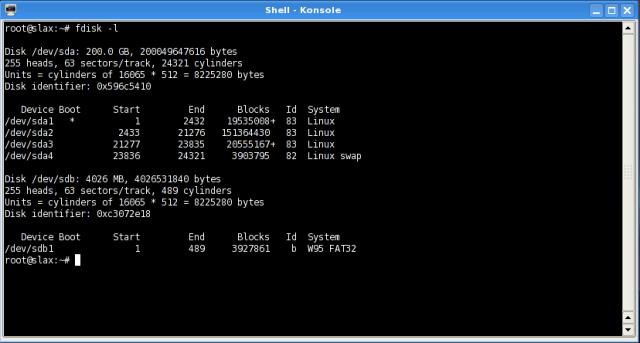
- Open a console ("Konsole" if you are using the KDE desktop), and type "fdisk -l" and read the list of drives and partitions. CAREFULLY IDENTIFY THE FLASH DRIVE! In this example, it is "sdb."
- Use Gparted (or QTParted) to reformat the flashdrive, and make it bootable. Select the FAT32 filesystem as the first or only partition if you want compatability with computers running Windows. If you want a separate partition for encryption, invisibility from Windows, or other features, set it up as a second partition after the FAT filesystem.
© 2005 - 2026 AB9IL.net, All Rights Reserved.
Written and curated by Philip Collier / AB9IL.
About Philip Collier / AB9IL, Commentaries and Op-Eds, Contact, Privacy Policy and Disclosures, XML Sitemap.